How Many Ribs Do We Have? Humans Ribs Anatomy
Everyone has heard of ribs and is familiar with the name as being either an important part of the human anatomy or…an amazingly delicious treat on the menu at some fancy restaurant. These bony rods in your body, fixed to your breast bone (sternum) are a natural protective cage.
Ribs exist to protect a person’s heart, lungs, spleen, and a large part of the liver. They also aid in shaping your chest cavity; responsible for assisting in breathing. Since their basic function is the protection of vital body organs, they are amongst the human body’s most important bones.
Ribs take the shape of a cage-like structure[1] enclosing the vital organs, hence they are collectively known as the rib cage. The effects of any broken ribs can be critical to the structure or working of the internal organs.
All vertebrates, and not just humans, have ribs. Nonetheless, humans are a complex species with a complex rib cage, consisting of the ribs and sternum. Another name for the rib cage is the thoracic cage, owing to its location in the chest or thorax.
In the front, ribs are joined to the sternum; in the back to the thoracic vertebrae. They also give support to the collarbone (pectoral girdle). The sternum lies in front of the vital organs. This is a strong bone and is not easy to crack, whereas the ribs can fracture easily.
Read on to discover more about how many ribs men and women have and why variations in the number of ribs can occur.
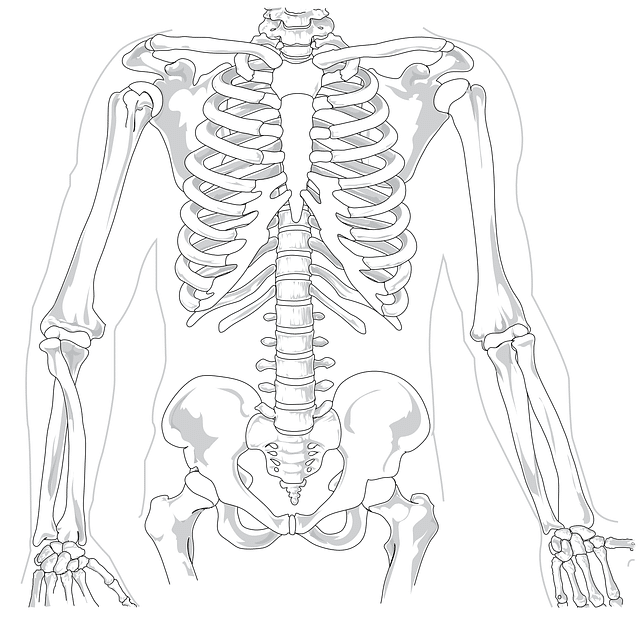
How Many Ribs Do Humans Have?
Most humans are born with 12 pairs of ribs…that’s 24 in all. Gender has nothing to do with this…it’s 12 ribs for everyone. Nonetheless, the female rib cage is believed to be around 10% smaller[2] in volume than that of a male of the same height.
The exception to this anatomy rule of men and women having the same number of ribs is linked to certain genetic abnormalities; existing at birth. This can be a case of having excess ribs (supernumerary ribs) or having too few (agenesis of ribs).
The ribs we have can be divided into three categories: true ribs, false ribs, and floating ribs; based on how they are joined to the sternum parts. The human skeleton has 12 pairs of ribs.
- Starting from the top, ribs 1 to 7 are referred to as “true ribs”, they are directly linked from the spine to the sternum.
- Followed by ribs 8 to 10, known as “false ribs”, they don’t join directly but are linked by cartilage to the sternum.
- Then come ribs 11 and 12, the “floating ribs”, these are smaller and are only joined to the spine in the back.
Ribs 7-10, in the center of the rib cage, can break more easily than the upper and lower ones. The collarbone acts as protection for the upper ribs. The lowest ribs are aided by their “floating” characteristic in safeguarding against damage.
Do Men and Women Have the Same Number of Ribs?
The fact that women have an extra rib is not true. Actually, in some cases, people have an extra rib called a cervical rib; resulting from the last cervical vertebra. This “extra rib” can exist on either side of the body or even on both sides. It can be a complete bone formation or just a boneless strand of tissue fiber.
The Cervical or “Extra” Rib
This extra rib is actually an abnormality, that exists from birth[3], and is rarely noticed until sometime later in life. It’s not always visible on any scans of the body, such as an X-ray or MRI, that may be performed.
In the case of a partially developed cervical rib, it can turn into a swelling seen as a lump within the neck or extend into a band of tissue fiber attached to the first true rib.
Indeed, many people who may have a cervical rib, don’t depict any symptoms and don’t even know that they have one. Others may go through uncomfortable experiences like neck pain or numbness. This is due to the cervical rib exerting pressure on blood vessels or nerve endings.
A condition known as thoracic outlet syndrome (TOC) may develop due to the presence of a cervical rib. It occurs in adulthood and is believed to affect more men than women. Nonetheless, TOS does not affect all people with a cervical rib.
Even though cervical ribs are a rare presence, research[4] has shown that they occur more in women than in men. Surgical removal of a rib or ribs can be performed in those adults showing symptoms of TOC.
Other Reasons Why the Number of Ribs Varies
- Down syndrome – this is a chromosomal disorder in which people who are born with the condition occasionally have one extra rib or lack the 12th rib. However, not all cases of Down syndrome are susceptible to changes in the number of ribs.
- Spondylocostal dysplasia – this occurs when the ribs and spine undergo an abnormal development. People affected by this condition at birth can have missing ribs or a fusion of ribs.
- Spondylothoracic dysplasia – this is also referred to as spondylothoracic dysostosis. In this congenital condition. Infants have fused ribs and vertebrae together with tiny chest cavities contributing to extreme problems with respiration.
- Goldenhar syndrome – this uncommon congenital condition affects the spine, ears, and eyes. In addition to other symptoms, babies can have fused, missing, or partially formed ribs.
Treatment
Prophetical stories of Adam and Eve have contributed to the idea of men having one less rib than women. All normal men and women have 12 sets or 24 ribs, regardless of their gender.
People can have certain congenital disorders resulting in too many or too few ribs; these conditions do not always need to be cured.
Rib abnormalities don’t require treatment if they are not causing any trouble like abnormal growth, difficulties in breathing, or pain; all that a doctor will recommend is watchful waiting.
[1] “File:Ribs animation.gif” by Wikipedia.
[2] “Sexual dimorphism of human ribs” by US National Library of Medicine.
[3] “Anatomy, Thorax, Cervical Rib” by US National Center for Biotechnology Information.
[4] Read more at Radiopaedia.org.
